This article concerns features under development and subject to change.
Lighting in Giro3D
Lighting is a crucial element in a 3D scene and helps enhance the readability of volumes and relief, particularly of the terrain.
Giro3D offers two lighting modes for terrains: simplified and realistic.
Simplified Lighting (hillshading)
👉 This lighting mode is only compatible with the Map entity in a projected coordinate system.
It is defined by a pair of values (azimuth, zenith) describing the position of the sun as perceived from the center of the scene. This mechanism is very similar to what is offered by QGIS, for example.
The advantage of this system is that it is very simple to use and familiar to users of mapping tools.
However, its major drawback is that it does not work with the globe mode, as the axis of the sun’s rays differs at each point on the globe (whereas it is consistent on a flat map).
Another disadvantage is the lack of support for multiple light sources as well as cast shadows.
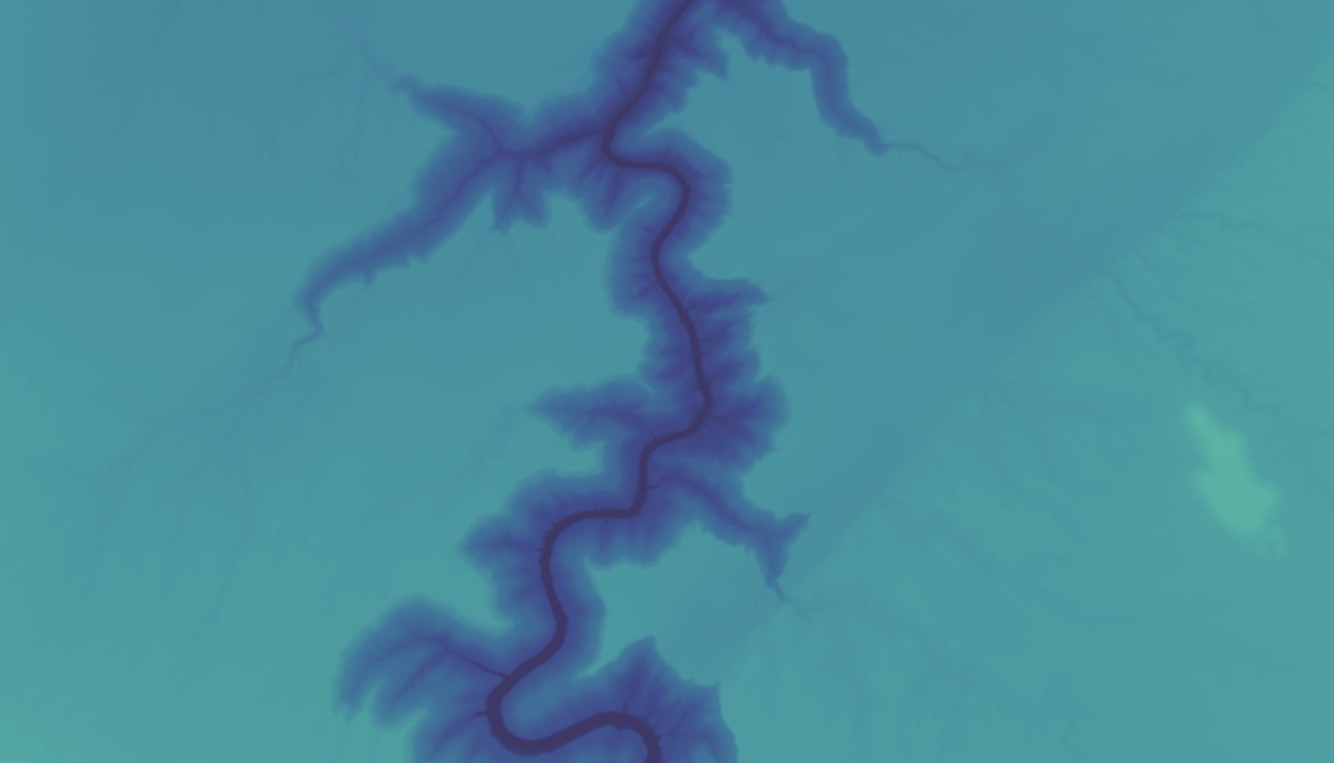
An elevation layer without active lighting
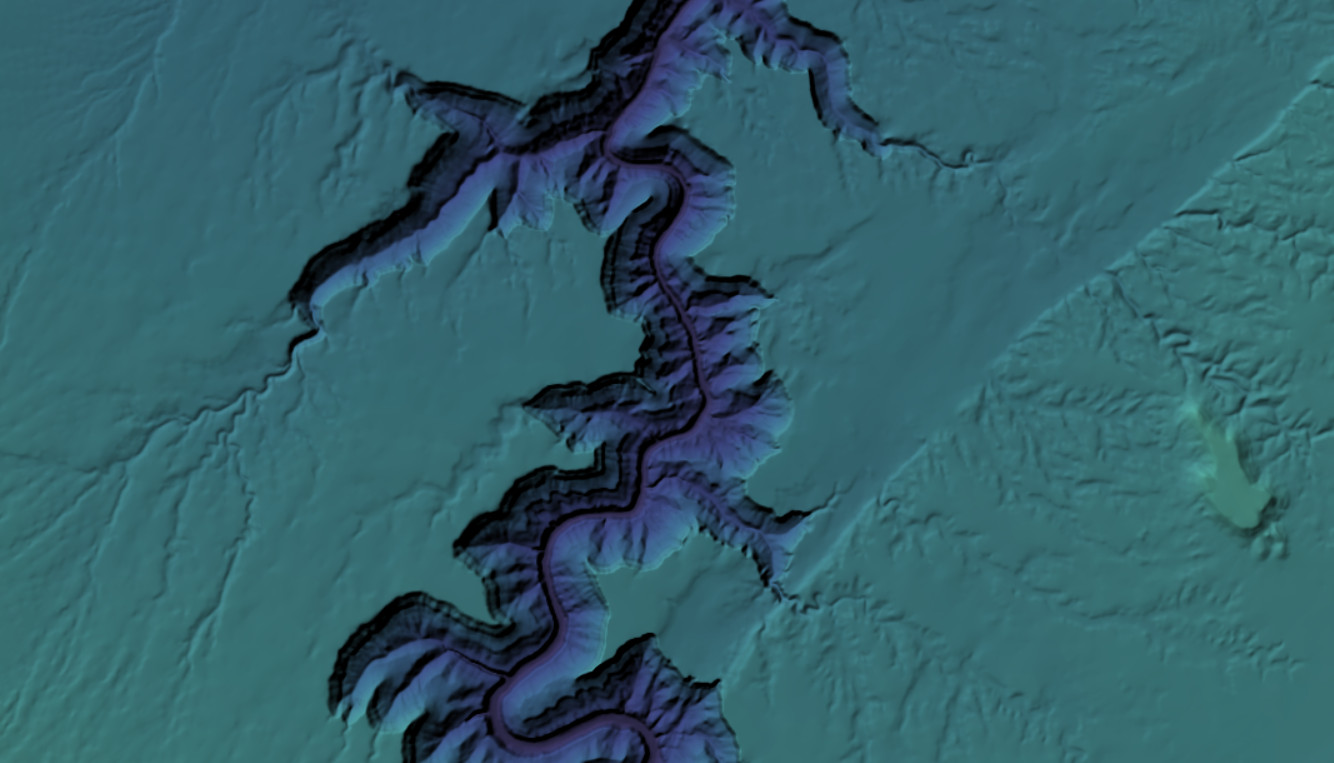

The same layer illuminated by simplified lighting
Realistic Lighting
👉 This lighting mode was previously not supported by the Map entity.
The realistic lighting mode uses the mechanisms of the three.js engine, such as physically-based rendering and cast shadows, to produce a more realistic scene.
This system allows for the use of an arbitrary number of light sources represented by 3D objects:
- Ambient light to simulate soft light without a specific source, like the sky,
- Directional light, notably used to simulate sunlight,
- Point lights to simulate light sources such as street lamps or other local artificial lighting.
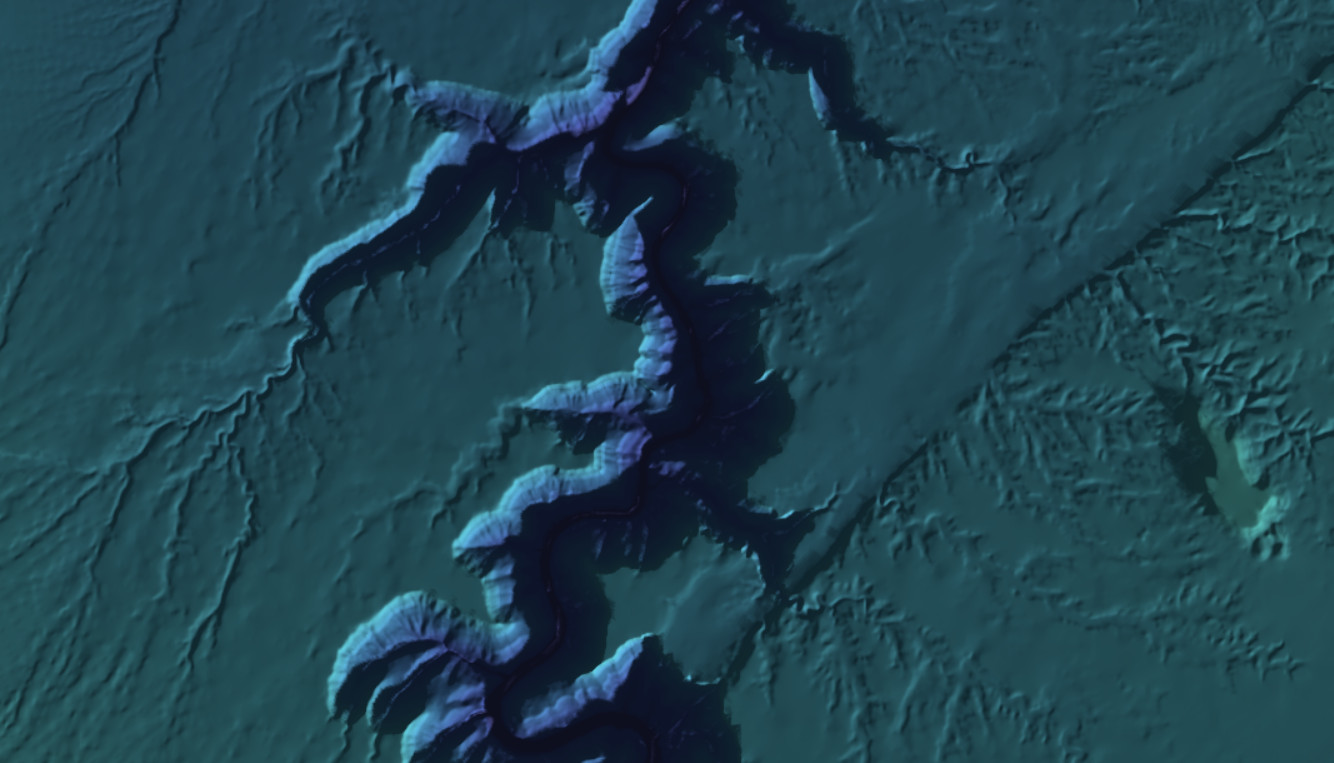

The same elevation layer illuminated by directional light, ambient light, and cast shadows
Cast Shadows
The realistic lighting system also makes it possible to visualize cast shadows, enabling numerous use cases, such as:
- visualizing sunlight exposure in a valley at a given time,
- visualizing shadows cast by buildings on a street.
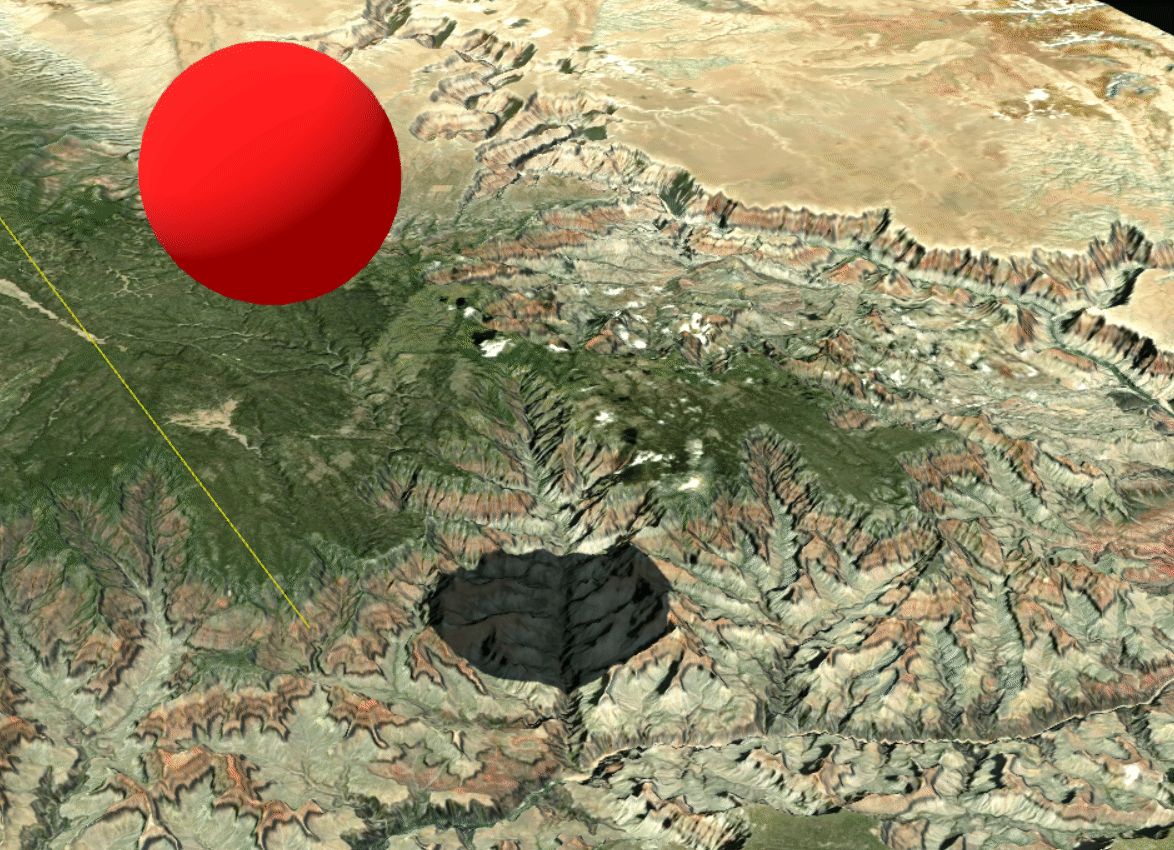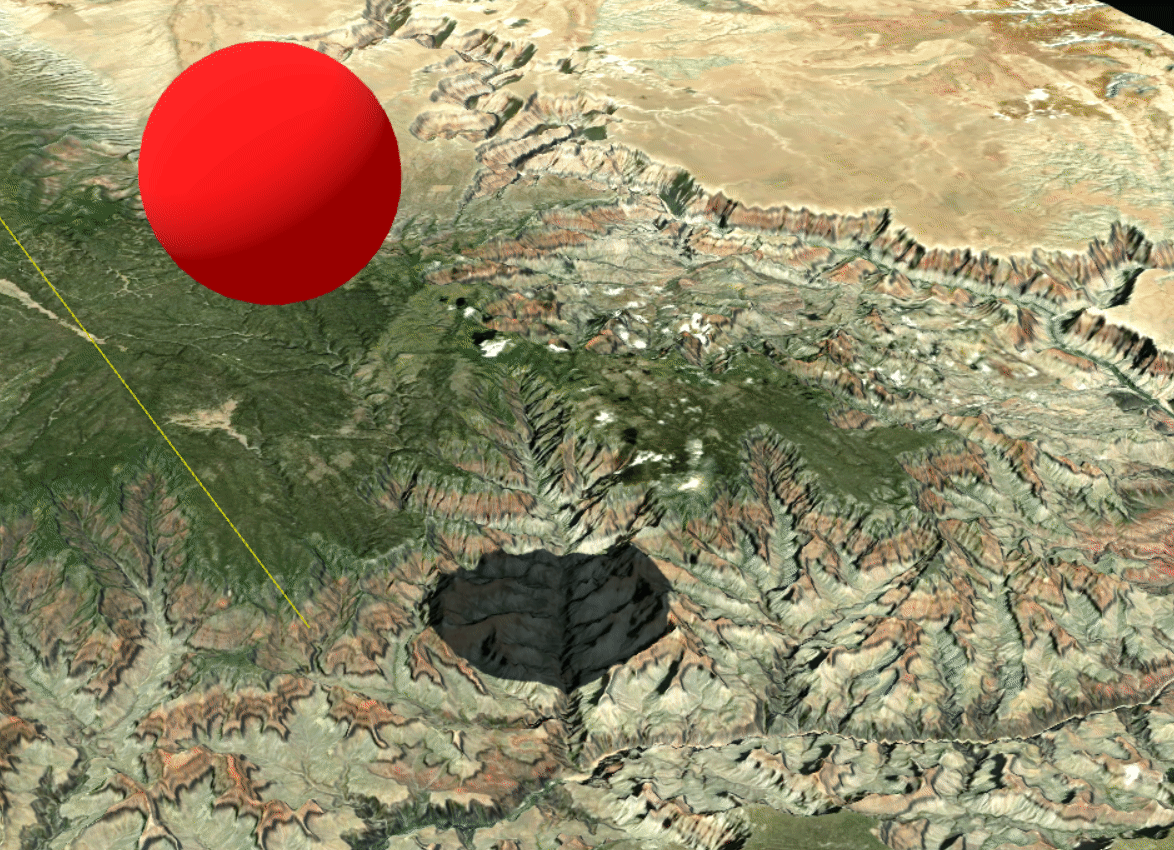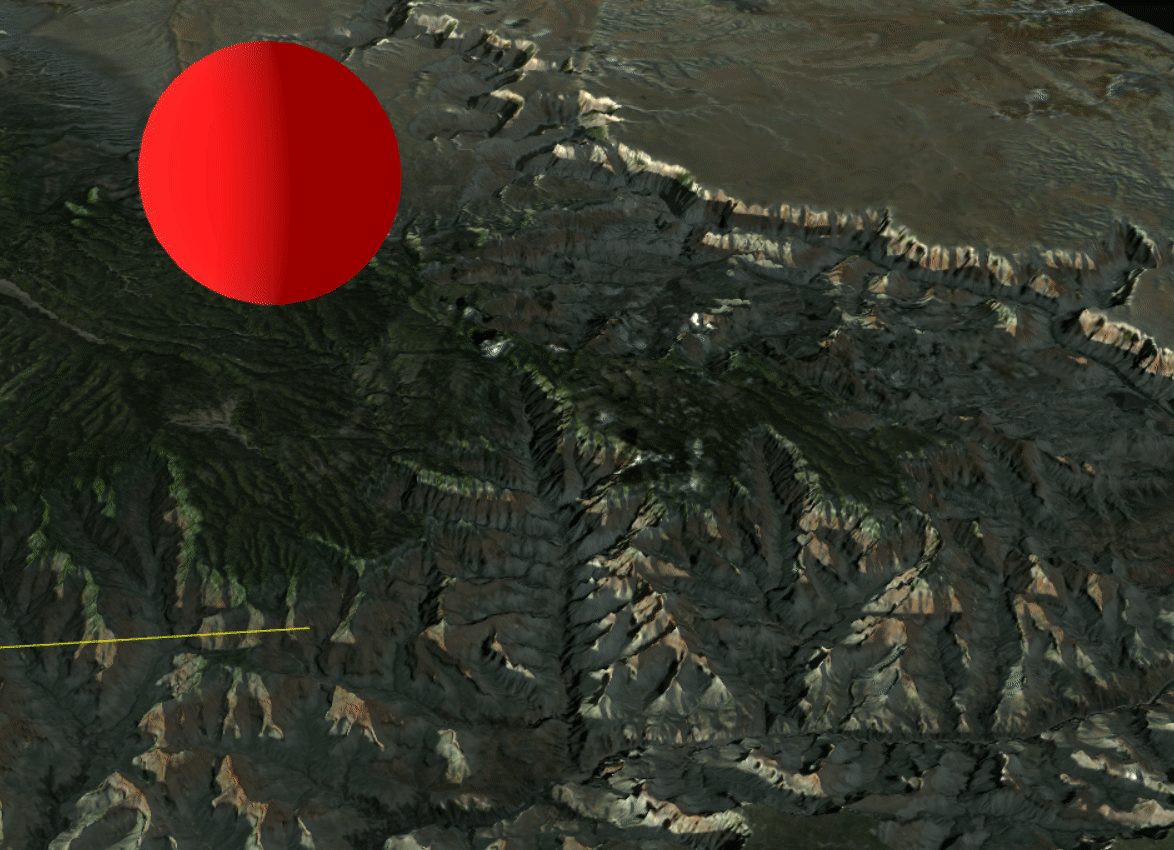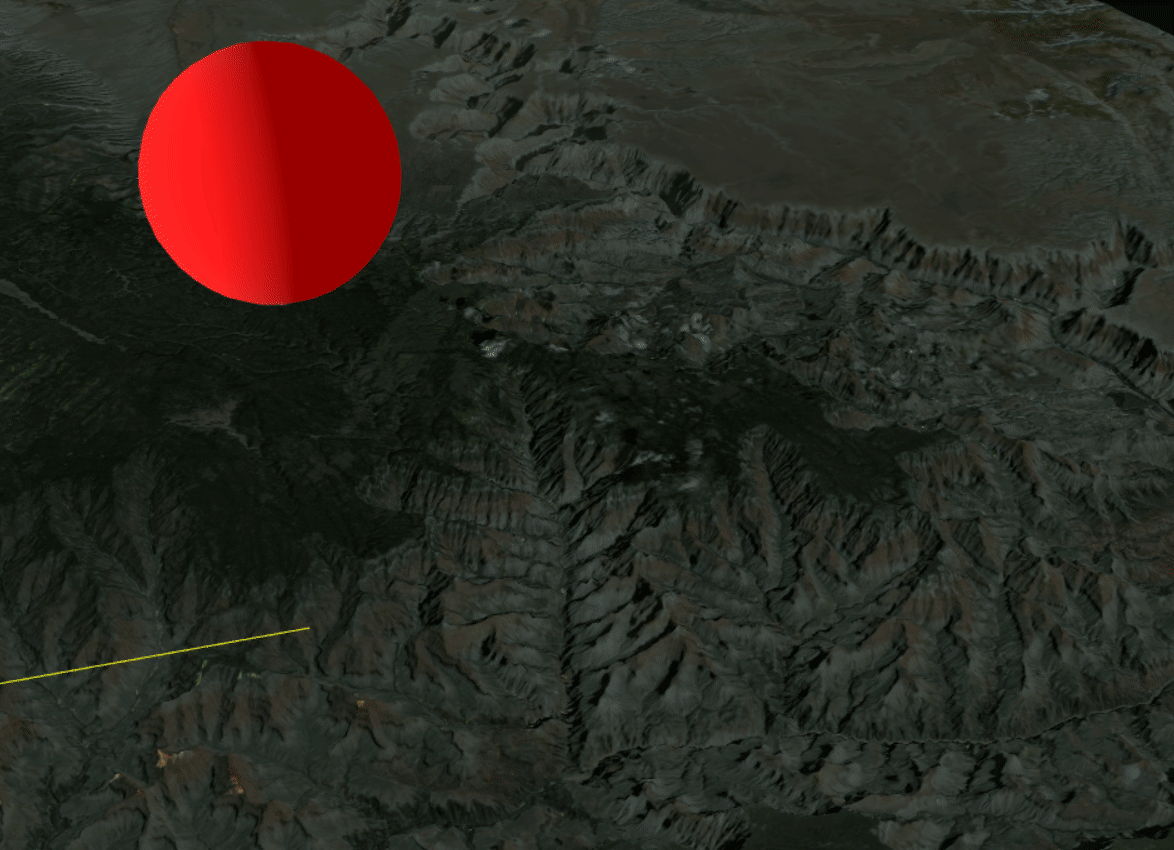
Shadows cast by the Grand Canyon combined with those of the sphere
Conclusion
Full support for three.js lighting for the Map entity aligns with Giro3D’s philosophy of integrating as seamlessly as possible into the three.js ecosystem.
Cast shadows represent an interesting addition for improving the visual quality of scenes and aiding decision-making in sunlight analyses.
Do not hesitate to visit Giro3D website, and do not miss the interactive examples page !
Should you want more information, discuss with Giro3D developers, share your needs or use cases, do not hesitate to contact us at infos+3d@oslandia.com ! We will be pleased to get in touch !


